Infection refers to the invasion and multiplication of various organisms that are normally not present in the body. As the name suggests, intestinal infection occurs when there is invasion and multiplication of organisms such as bacteria, viruses and parasites.
Causes of Intestinal Infection
The causative agents of intestinal infections include the following:
- Bacteria
- E coli: E. Coli are gram negative bacteria which are normally found in the intestines of animals and people.
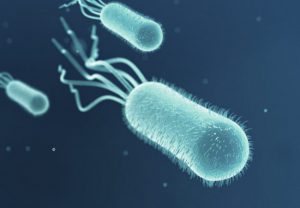
E. Coli (source: health.clevelandclinic.org) Although most varieties don’t cause any harm, some strains are known to secrete harmful toxins. These toxins cause diarrhea, vomiting and cramps. These E.Coli can spread through direct person-to-person contact or through infected food or water.
- Salmonella: Salmonella bacteria generally live in human and animal bowels and are excreted through feces. Salmonellosis(salmonella infection) is mainly cause by ingestion of undercooked poultry, meat and eggs.
- Viruses:
- Rotavirus: Rotavirus is the most common causative organism of viral gastroenteritis affecting children. This is usually due to children touching contaminated items and then putting those fingers into their mouths.
- Norovirus: Norovirus most commonly spreads in people confined to small places. Although this virus spreads mostly from through water or food, person-to-person has also occurred in the past.
- Parasites
- Cryptosporidium: It is a type of microscopic parasite and is one of the major causes of waterborne diseases in the United States. Due to its outer shell, it is able to survive several harsh conditions.
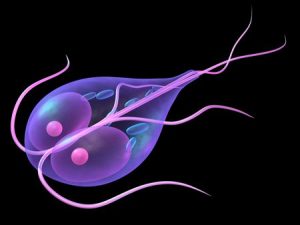
Giardia (source: www.thesprucepets.com) - Giardia: It is another microscopic parasite which causes diarrheal disease known as giardiasis. It may be found in the soil, water or food that has been contaminated with feces of other infected persons or animals.
Effects and Symptoms
The pathogens enter the gastrointestinal tract and can produce several toxins which then cause damage to the lining cells of the gastrointestinal tract. Since these cells are important for proper absorption and electrolyte balance, the following symptoms can be seen when you suffer from a gastrointestinal infection.
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Stomach Ache
- Dehydration(excessive thirst, dry coated tongue, yellow urine, dizziness, weakness)
- Loose Stools
- Mucus of Blood-mixed Stools
- Muscle Pain
- Weight Loss
Prevention and Cure
Treatment for gastrointestinal infections include:

- Home remedies include- drinking adequate fluids, eat little but frequent meals including salty foods, consume potassium-rich foods such as bananas and juices, ginger can help fight off the infection and apple cider vinegar can cause a soothing effect on your stomach too
- Oral rehydration solution can help prevent dehydration
- IV fluids and salts may be given to you at the hospital
- It is a good idea to visit the doctor in order to determine which medicines to take- the doctor will probably recommend antibiotics in severe cases(such as penicillin, cephalosporin, nitroimidazole and monobactam antibiotics)
Ways to prevent future episodes of gastrointestinal infections include:
- Wash your hands properly and frequently, especially before handling food
- Avoid close contact with other infected people or animals
- Avoid raw meats and unpasteurized milk
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consuming
- Store food properly and at very high or low temperatures in which organisms cannot survive
- Drink boiled or filtered water
- Try to keep your kitchen clean